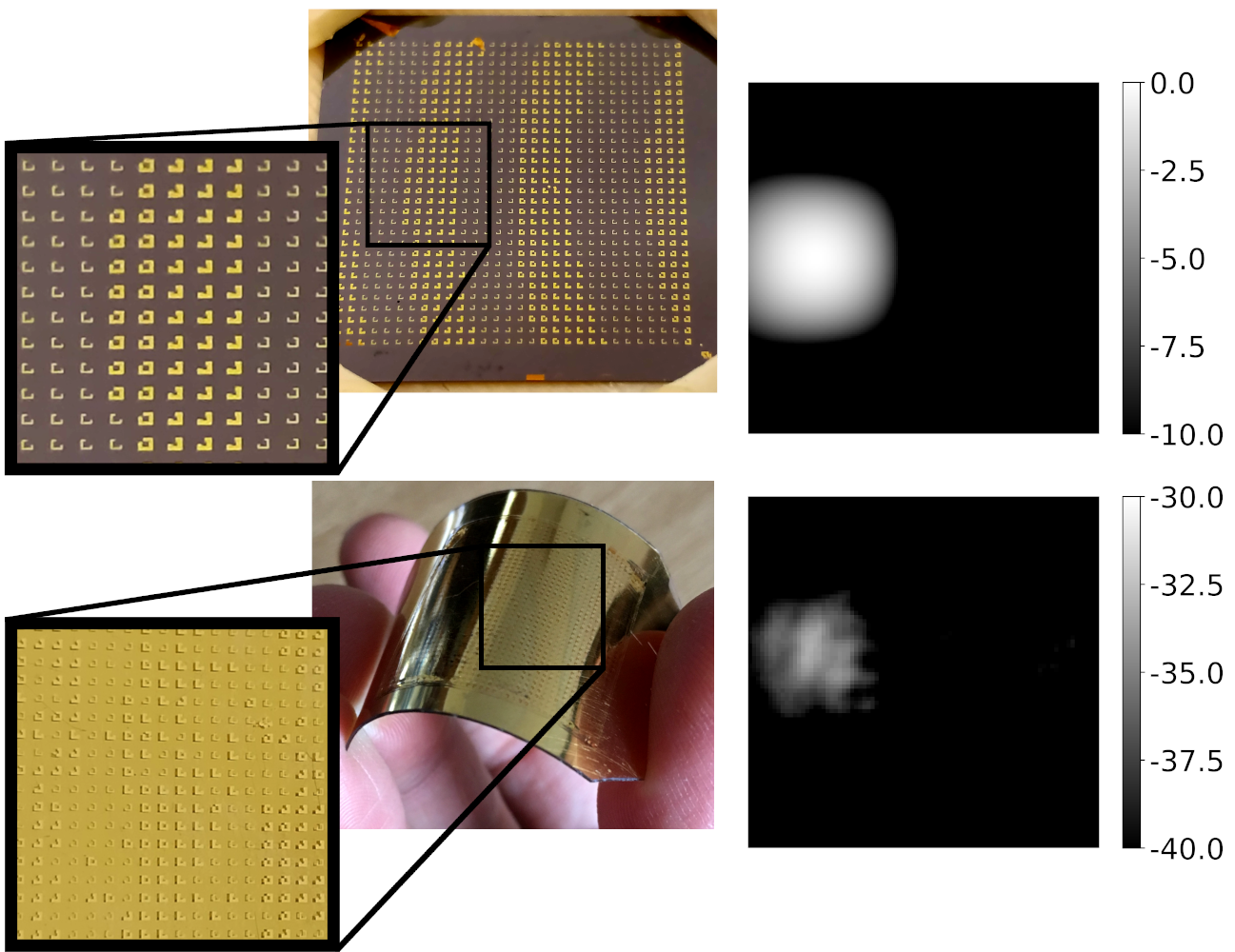
ERC PoC – Holophrase
[Edit February 2023: Holophrase is now funded by the EPSRC, due to the UK-EU ongoing negotiations.] We are happy to share the news that the group has been awarded an ERC Proof of Concept grant, to develop an integrated on-chip pH sensor. HolopHrase is based on the ERC consolidator grant AMPHIBIANS, which introduces the metasurfaces technology in microfluidic environments. With HolopHrase, we will develop a flexible solution for the real time, label free, quantitative optical imaging readout of the pH level of a liquid solution. Our approach brings together the ease of access, simplicity, and cost of bulkier solutions, with the accuracy and level of… Read More »ERC PoC – Holophrase