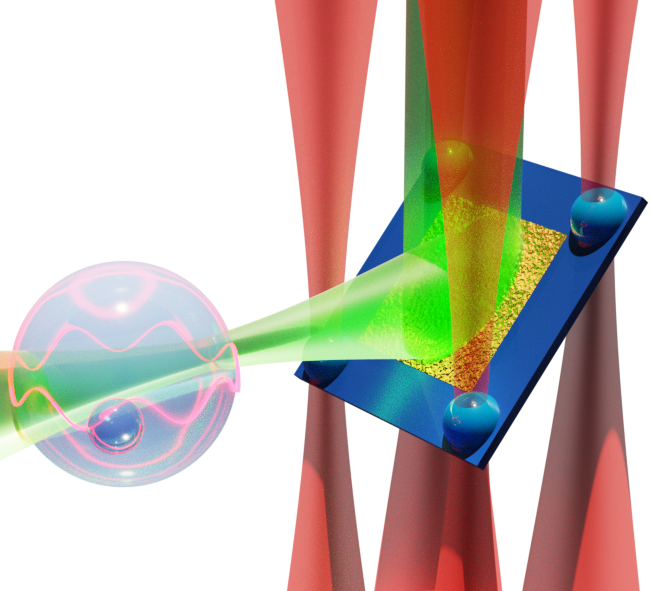
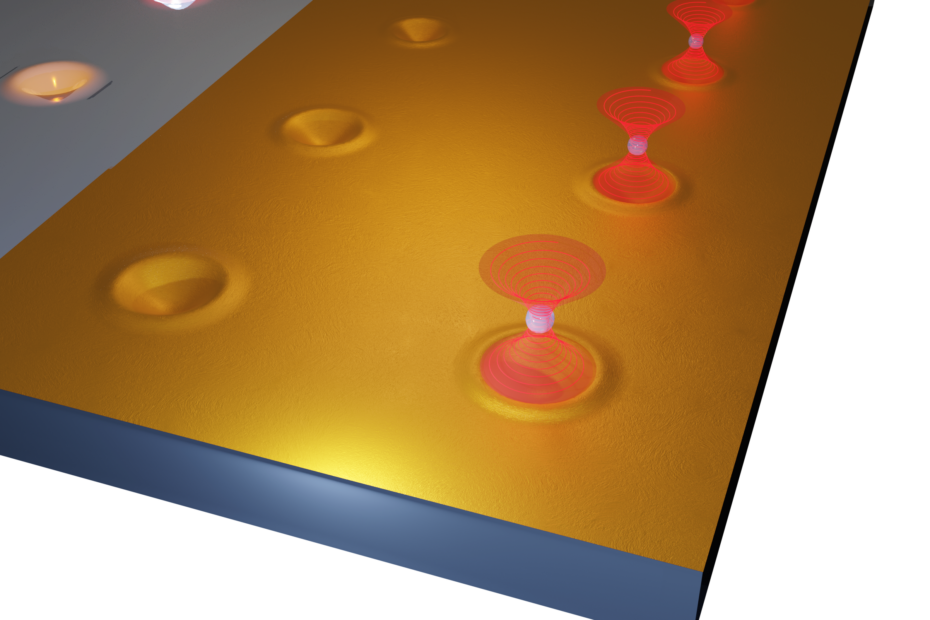
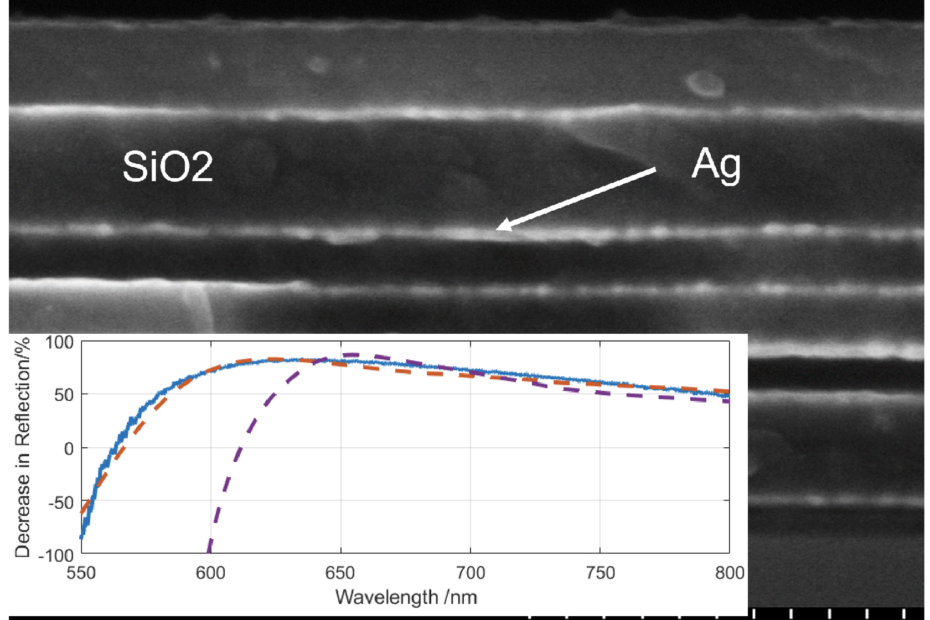
Optically Manipulated Micromirrors for Precise Excitation of WGM Microlasers
Whispering gallery mode microlasers are highly-sensitive refractive index sensors that are widely explored for biophotonic and biomedical applications. These microlasers are used for excitation and collection of the emitted light, typically utilizing microscope objectives at normal incidence. However, this limits the choice of the oscillation plane of the modes. To overcome this limitation, in this paper, we present a new platform that enables the excitation of microlasers from various directions using an optically manipulated micromirror. This scheme enables precise sensing of the environment surrounding the microlasers along different well-controlled planes. Furthermore, the platform’s capability to perform a time-resolved experiment of dynamic sensing using a polystyrene… Read More »Optically Manipulated Micromirrors for Precise Excitation of WGM Microlasers